What is EBS?
Amazon Elastic Block Store (AWS EBS) is a raw block-level storage service designed to be used with Amazon EC2 instances. When mounted to Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon EBS volumes can be used like any other raw block device: they can be formatted with a specific file system, host operating systems, and applications, and have snapshots or clones made from them.
This means that the data is kept on the AWS EBS servers even when the EC2 instances are shut down. The data volumes can be dynamically attached, detached, and scaled with any EC2 instance, just like a physical block storage drive. As a highly dependable cloud service, the EBS offering guarantees 99.999% availability.
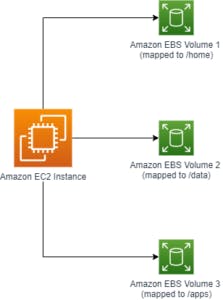
The image below shows a logical representation of Amazon EBS: Where Amazon EBS Volumes are Attached to an Amazon EC2 Instance
Types of EBS
There are two Amazon EBS volume type categories:
SSD-backed volumes and HDD-backed volumes
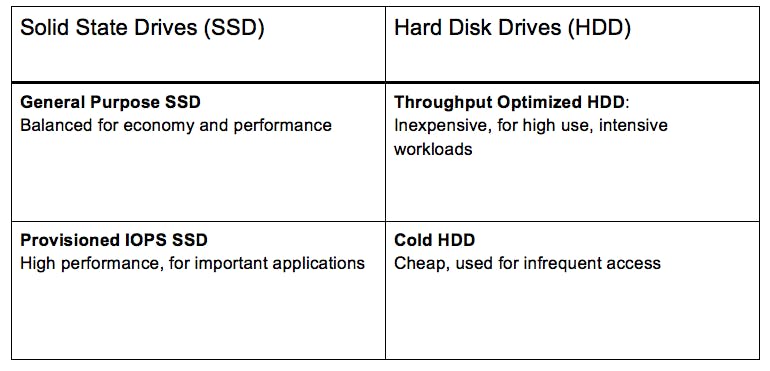
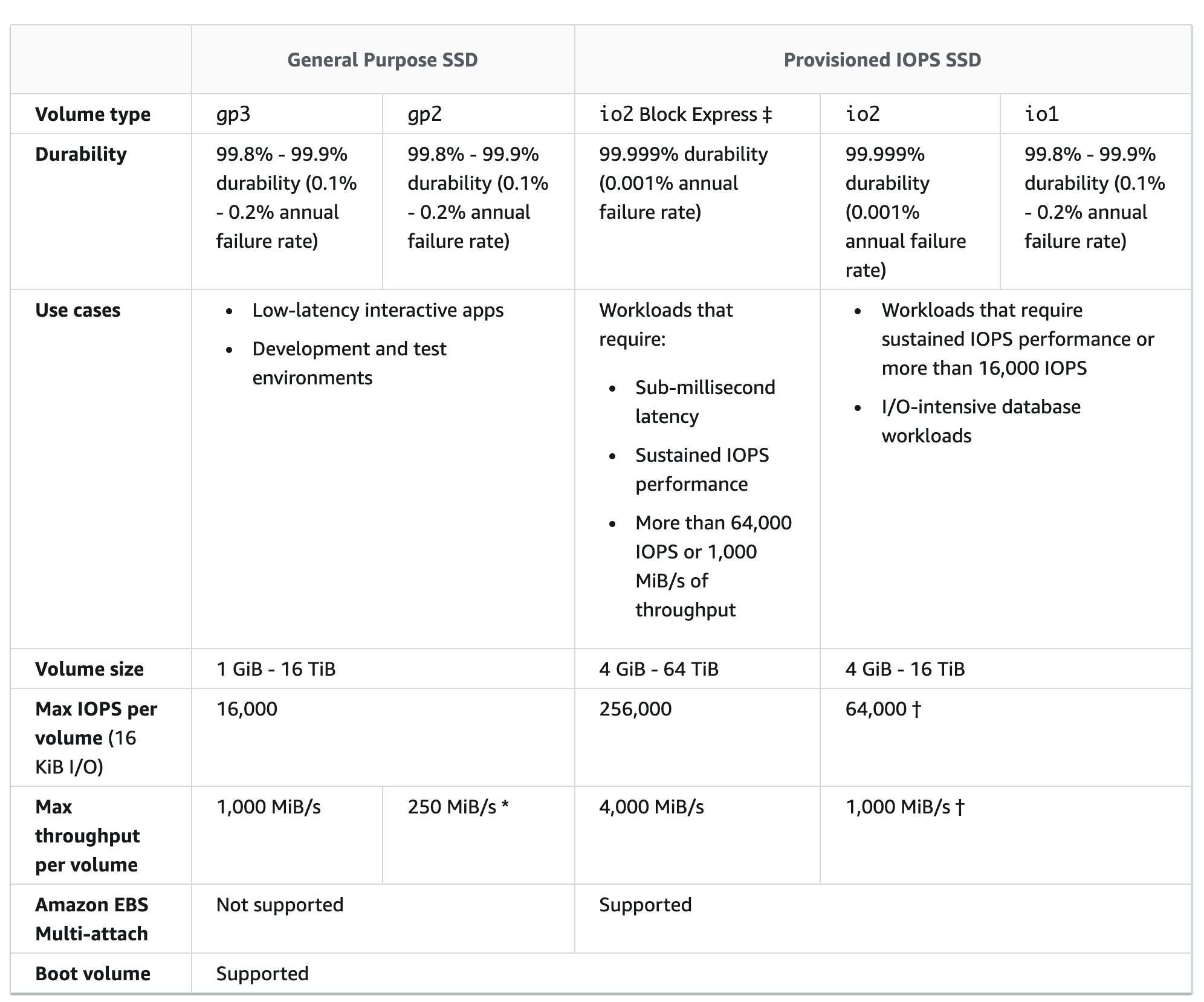
The SSD-backed volumes provided by Amazon EBS fall into these categories:
General Purpose SSD — Provides a balance of price and performance. We recommend these volumes for most workloads.
Provisioned IOPS SSD — Provides high performance for mission-critical, low-latency, or high-throughput workloads.
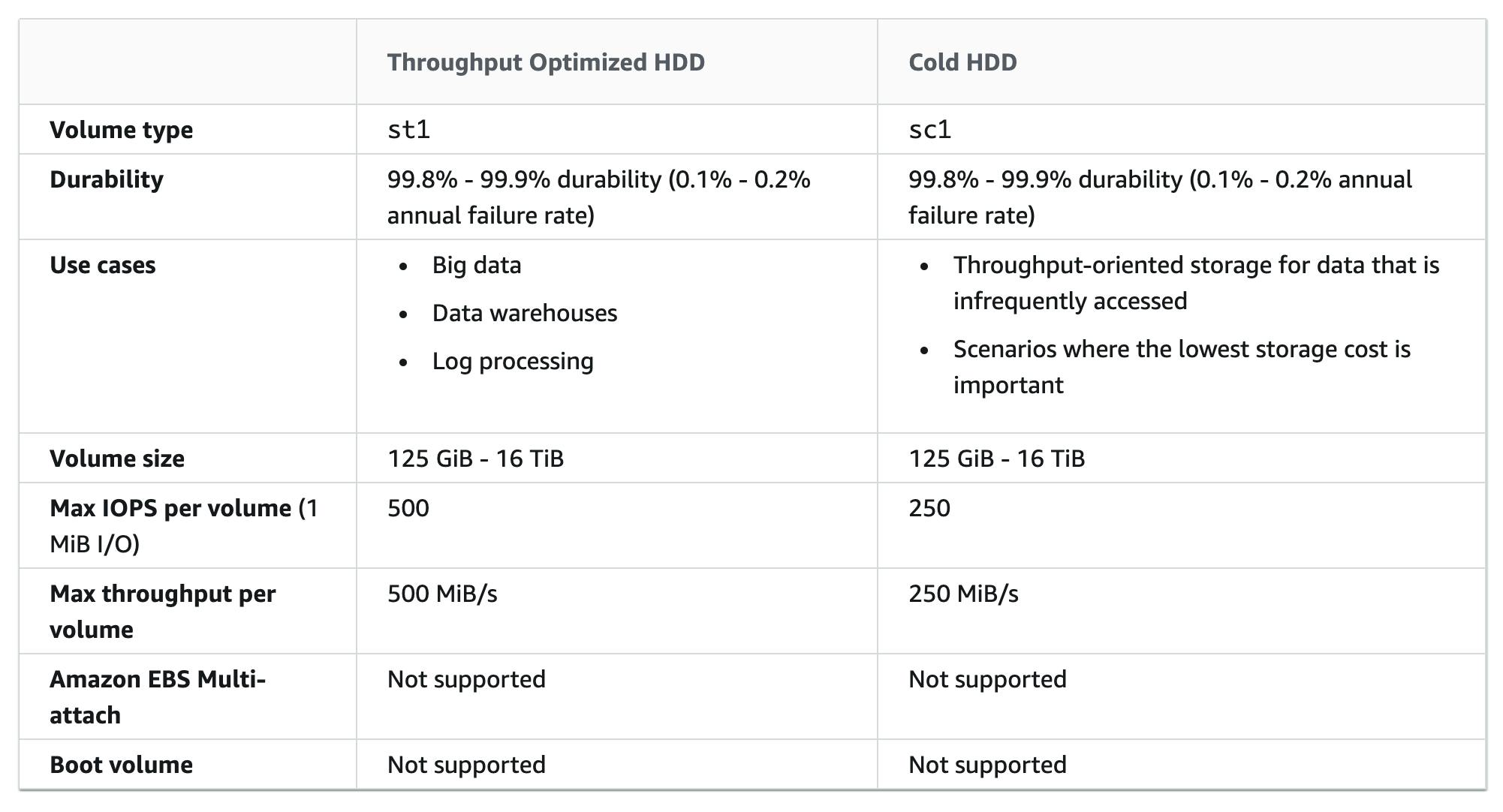
The HDD-backed volumes provided by Amazon EBS fall into these categories:
Throughput Optimized HDD — A low-cost HDD designed for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads.
Cold HDD — The lowest-cost HDD design for less frequently accessed workloads.
What Is AWS EFS?
AWS Elastic File System (EFS) is one of the three main storage services offered by Amazon. It is a scalable, cloud-based file system for Linux-based applications and workloads that can be used in combination with AWS cloud services and on-premise resources.
EFS offers a choice between two storage classes, Infrequent Access, and Standard access, depending on your needs.
- Standard access storage is designed for frequently accessed files.
- Infrequent Access is intended for storing long-lived but less used files at a lower cost.
The image below shows a logical representation of Amazon EFS: Where An Amazon EFS Volume is Mounted on Multiple EC2 Instances
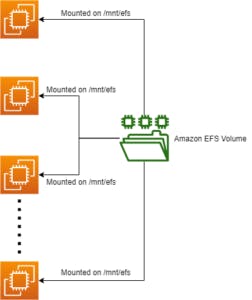
Advantages of using EFS:
- A single EFS can be mounted to multiple EC2 instances across multiple Availability Zones.
- The EFS volume can be scaled automatically whenever files or folders are added or deleted from the system.
- EFS storage is permanent meaning that the data stored in EFS won’t be lost when the EC2 instances is terminated.
Amazon EBS vs. Amazon EFS
The difference between using Amazon EBS and using Amazon EFS can be compared to parking a car in a home garage versus parking a car in a rental parking lot. Using Amazon EBS is like parking in your own private garage: you tend to use your car frequently and the space is highly secure. Using Amazon EFS is more like parking in a big rental parking lot: there are lots of people, including yourself, sharing a common space available to accommodate a large number of individuals.
Amazon EBS is generally used for persistent block storage. It is ideal for databases and other low-latency interactive applications that require high IOPS or throughput, and specifically low latency with consistent and predictable performance. Now, there is an argument that you can use Amazon EFS instead of Amazon EBS, so you won’t have to worry about space. But, returning to our analogy, building a huge parking lot to have extra space just for your car is not a smart idea: it will cost more, and the space will go unused. Plus, Amazon EBS volumes can scale up or down with a single API call and without stopping the instance.
So, when is it a good idea to use Amazon EFS? Amazon EFS is designed for the huge amounts of data that big data workloads and analytic applications generate; amounts of data that are so large it is impossible for an Amazon EBS EC2 instance to access for processing or analysis. Because of that, Amazon EFS outweighs Amazon EBS in media processing workflows, content management, and web serving, even though Amazon EBS costs less.
Storage Cost(EBS and EFS)
Amazon EBS pricing:
- General Purpose SSD (gp2) $0.10 per GB-month
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1) $0.125 per GB-month ($0.065 per provisioned IOPS-month)
- Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) $0.045 per GB-month Cold HDD (sc1) volumes $0.025 per GB-month
Amazon EFS pricing:
- $0.30 GB-month ($6.00 per provisioned MB/s-month)
