What is Amazon VPC?
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) enables you to launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you've defined.
You have complete control over your virtual networking environment, including a selection of your IP address range, the creation of subnets, and the configuration of route tables and network gateways.
You can easily customize the network configuration for your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud. You can also provide multiple layers of security, including security groups and network access control lists, to help control access to Amazon EC2 instances in each subnet.
How VPCs work
Each VPC creates an isolated virtual network environment in the AWS cloud, dedicated to your AWS account. Other AWS resources and services operate inside of VPC networks to provide cloud services.
Using VPC, you can quickly spin up a virtual network infrastructure that AWS instances can be launched into. Each VPC defines what your AWS resources need, including:
- IP addresses
- Subnets
- Routing
- Security
- Networking functionality
Architecture of VPC
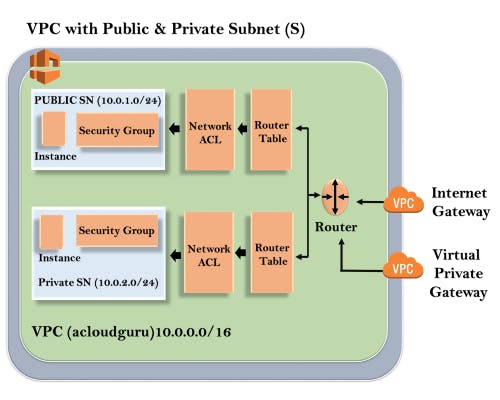
The outer line represents the region, and the region is us-east-1. Inside the region, we have VPC, and outside the VPC, we have an internet gateway and a virtual private gateway.
Internet Gateway and Virtual Private Gateway are the ways of connecting to the VPC. Both these connections go to the router in a VPC and then the router directs the traffic to the route table.
- Route table will then direct the traffic to Network ACL. Network ACL is the firewall or much like security groups. Network ACL are statelist which allows as well as denies the roles. You can also block the IP address on your Network ACL.
- Now, move over to the security group that accesses another line against the EC2 instance.
- It has two subnets, i.e., Public and Private subnet. In a public subnet, the internet is accessible by an EC2 instance, but in a private subnet, an EC2 instance cannot access the internet on its own. We can connect the instances.
- To connect an instance, move over to the public subnet and then SSH to the private subnet. This is known as jump boxes. In this way, we can connect an instance in a public subnet to an instance in a private subnet.
Elements of a VPC
VPC network services include:
- IPv4 and IPv6 address blocks
- Subnet creation
- Route tables
- Internet Gateway
- Elastic IP addresses (EIPs)
- Network/subnet security
- Additional networking services
IPv4 and IPv6 address blocks
VPC IP address ranges are defined using Classless interdomain routing (CIDR) IPv4 and IPv6 blocks. You can add primary and secondary CIDR blocks to your VPC, if the secondary CIDR block comes from the same address range as the primary block.
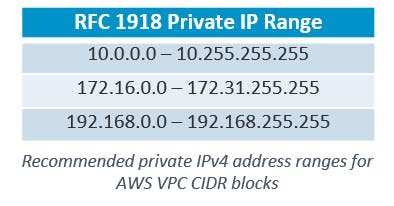
AWS recommends that you specify CIDR blocks from the private address ranges specified in RFC 1918, shown in the table below.
Subnet creation
A subnet is a range of IP addresses in your VPC. You can launch AWS resources, such as EC2 instances, into a specific subnet. When you create a subnet, you specify the IPv4 CIDR block for the subnet, which is a subset of the VPC CIDR block. Each subnet must reside entirely within one Availability Zone and cannot span zones. By launching instances in separate Availability Zones, you can protect your applications from the failure of a single zone.
Route tables
Route tables contain the rules (routes) that determine how network traffic is directed inside your VPC and subnets. VPC creates a default route table called the main route table. The main route table is automatically associated with all VPC subnets. Here, you have two options:
- Update and use the main route table to direct network traffic.
- Create your own route table to be used for individual subnet traffic.
Internet Gateway
An internet gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that allows communication between your VPC and the internet. An internet gateway enables resources (like EC2 instances) in your public subnets to connect to the internet if the resource has a public IPv4 address or an IPv6 address. Similarly, resources on the internet can initiate a connection to resources in your subnet using the public IPv4 address or IPv6 address. For example, an internet gateway enables you to connect to an EC2 instance in AWS using your local computer.
An internet gateway serves two purposes: to provide a target in your VPC route tables for internet-routable traffic, and to perform network address translation (NAT) for instances that have been assigned public IPv4 addresses.
An internet gateway supports IPv4 and IPv6 traffic. It does not cause availability risks or bandwidth constraints on your network traffic. There's no additional charge for having an internet gateway in your account.
Elastic IP addresses (EIPs)
An Elastic IP address is a static, public IPv4 address designed for dynamic cloud computing. You can associate an Elastic IP address with any instance or network interface in any VPC in your account. With an Elastic IP address, you can mask the failure of an instance by rapidly remapping the address to another instance in your VPC.
Network/subnet security
VPCs use security groups to provide stateful protection (the state of the connection session is maintained) for instances. AWS describes security groups as virtual firewalls.
VPCs also provide network access control lists (NACLs) to stateless VPC subnets—that is, the state of the connection is not maintained.
What can we do with a VPC?
- Launch instances in a subnet of your choosing. We can choose our own subnet addressing.
- We can assign custom IP address ranges in each subnet.
- We can configure route tables between subnets.
- We can create an internet gateway and attach it to our VPC.
- It provides much better security control over your AWS resources.
- We can assign security groups to individual instances.
- We also have subnet network access control lists (ACLS).
VPC Peering
A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them privately. Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network. You can create a VPC peering connection between your own VPCs, with a VPC in another AWS account, or with a VPC in a different AWS Region.
VPC Endpoint
- A VPC endpoint allows you to privately connect your VPC to supported AWS services and VPC endpoint services powered by PrivateLink without requiring an internet gateway, NAT device, VPN Connection, or AWS Direct Connect connection.
- Instances in your VPC do not require public addresses to communicate with the resources in the service. Traffic between your VPC and the other service does not leave the Amazon network.
- VPC endpoints are virtual devices.
- VPC Endpoints are horizontally scaled, redundant and highly available VPC components that allow communication between instances in your VPC and services without imposing availability risks or bandwidth constraints on your network traffic.
